Concepts
LlamaIndex.TS helps you build LLM-powered applications (e.g. Q&A, chatbot) over custom data.
In this high-level concepts guide, you will learn:
- how an LLM can answer questions using your own data.
- key concepts and modules in LlamaIndex.TS for composing your own query pipeline.
Answering Questions Across Your Data
LlamaIndex uses a two stage method when using an LLM with your data:
- indexing stage: preparing a knowledge base, and
- querying stage: retrieving relevant context from the knowledge to assist the LLM in responding to a question
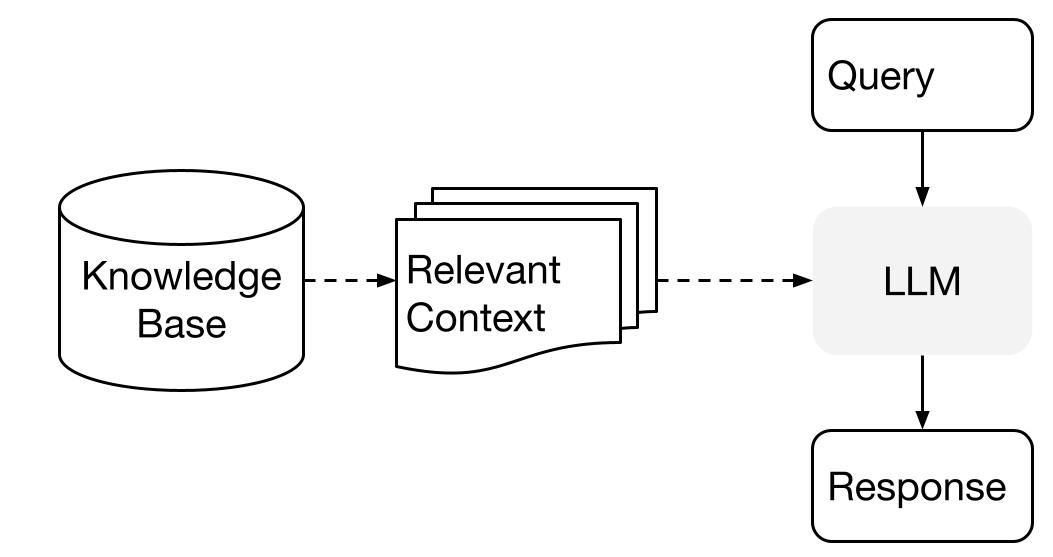
This process is also known as Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
LlamaIndex.TS provides the essential toolkit for making both steps super easy.
Let's explore each stage in detail.
Indexing Stage
LlamaIndex.TS help you prepare the knowledge base with a suite of data connectors and indexes.

Data Loaders:
A data connector (i.e. Reader) ingest data from different data sources and data formats into a simple Document representation (text and simple metadata).
Documents / Nodes: A Document is a generic container around any data source - for instance, a PDF, an API output, or retrieved data from a database. A Node is the atomic unit of data in LlamaIndex and represents a "chunk" of a source Document. It's a rich representation that includes metadata and relationships (to other nodes) to enable accurate and expressive retrieval operations.
Data Indexes: Once you've ingested your data, LlamaIndex helps you index data into a format that's easy to retrieve.
Under the hood, LlamaIndex parses the raw documents into intermediate representations, calculates vector embeddings, and stores your data in-memory or to disk.
Querying Stage
In the querying stage, the query pipeline retrieves the most relevant context given a user query, and pass that to the LLM (along with the query) to synthesize a response.
This gives the LLM up-to-date knowledge that is not in its original training data, (also reducing hallucination).
The key challenge in the querying stage is retrieval, orchestration, and reasoning over (potentially many) knowledge bases.
LlamaIndex provides composable modules that help you build and integrate RAG pipelines for Q&A (query engine), chatbot (chat engine), or as part of an agent.
These building blocks can be customized to reflect ranking preferences, as well as composed to reason over multiple knowledge bases in a structured way.
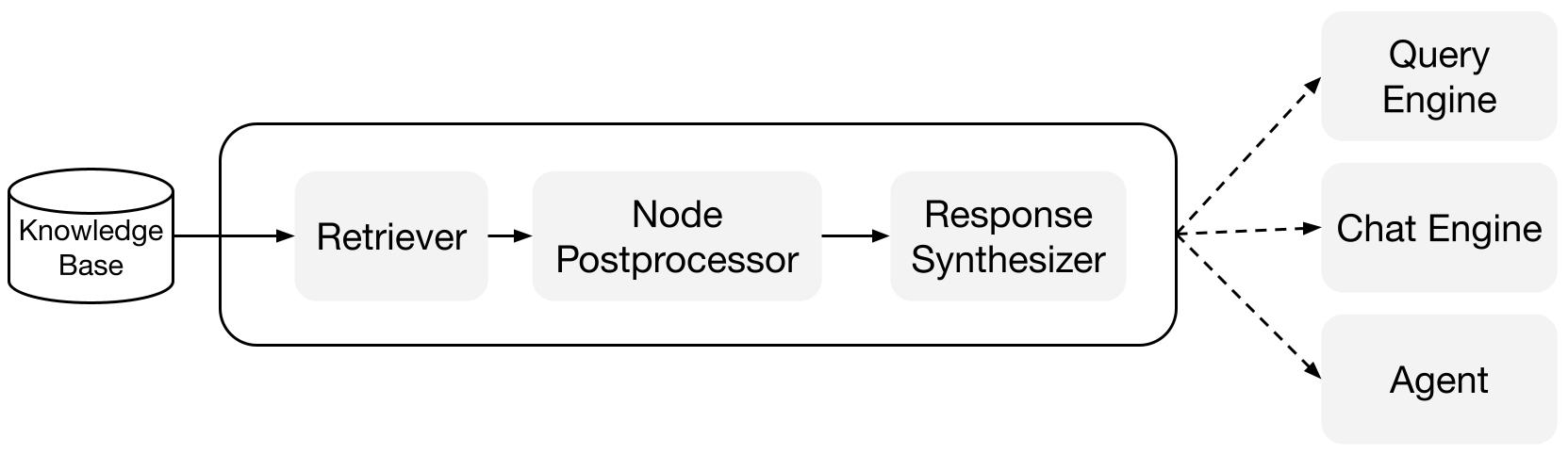
Building Blocks
Retrievers: A retriever defines how to efficiently retrieve relevant context from a knowledge base (i.e. index) when given a query. The specific retrieval logic differs for different indices, the most popular being dense retrieval against a vector index.
Response Synthesizers: A response synthesizer generates a response from an LLM, using a user query and a given set of retrieved text chunks.
Pipelines
Query Engines: A query engine is an end-to-end pipeline that allow you to ask question over your data. It takes in a natural language query, and returns a response, along with reference context retrieved and passed to the LLM.
Chat Engines: A chat engine is an end-to-end pipeline for having a conversation with your data (multiple back-and-forth instead of a single question & answer).